Sectorial analysis
The sector analysis allows to know the level of competitiveness that a company has within the sector in which it competes.
To begin, every company needs to know some fundamental points of the sector in which it competes. One of the most important is to know who are the competitors that you face, in addition to knowing who are the consumers of the sector, what suppliers exist in the market or the barriers that exist in that sector. It is also important to know the expected level of profitability.
Indeed, sectoral analysis can be performed using Porter's 5 forces model. This model gives us the key answers to achieve the success of the company within a competitive sector. It is important to clarify that sector analysis is not the same as market analysis. The sector analysis helps the company to develop its business plan. This plan will help you outperform your competitors and focus on a specific segment, to better serve it.
What is a sector?
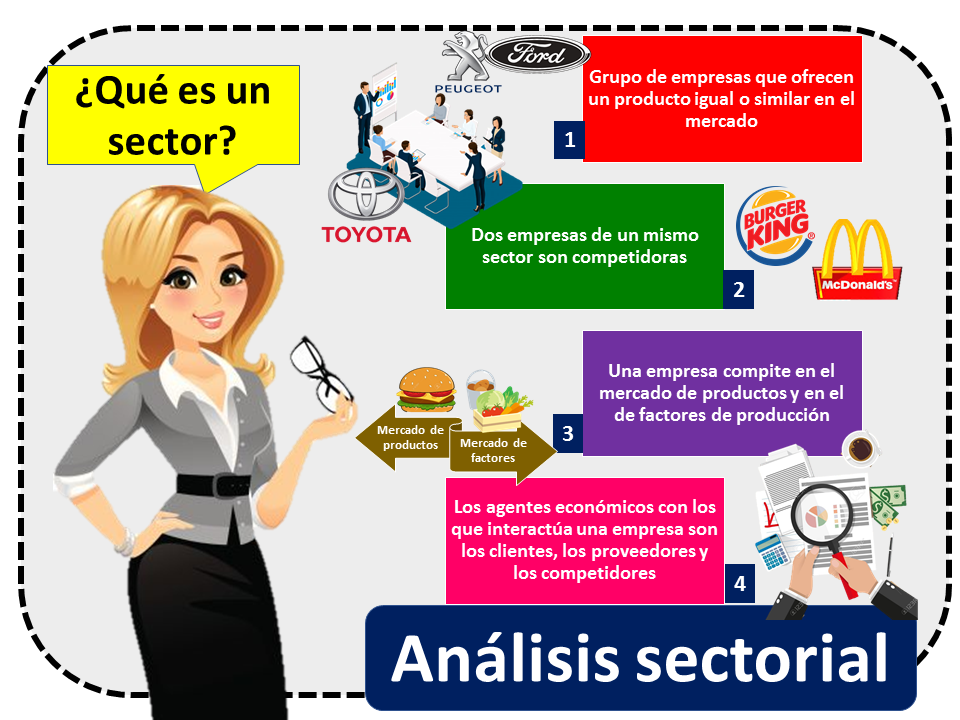
Above all, a sector is a group or set of companies that offer the same product or a similar product to the market. When two companies belong to the same sector, they become competing companies.
It is important to note that the profitability of a sector is determined by the level of competition that exists, and competition is established in two different markets. A company has competitors in the product market and in the market for factors of production.
Of course, each of these markets requires a separate analysis. It is also necessary to know the agents that interact in these markets. The economic agents with which a company has to interact are suppliers, customers and competitors. In addition, the environment of the national and international economy and the available resources must be considered in a sector.

Important factors taken into account in the sector analysis
When conducting a sectoral analysis, the following factors should be taken into account:
1. Clients' bargaining power
First, one of the essential factors in a sector analysis is knowing the clients of the sector. Clients 'bargaining power refers to our clients' ability to obtain better product conditions and lower prices.
Customers have more bargaining power when there are many companies that offer similar or substitute products, since this allows buyers to have a greater choice. In addition, if they are customers who buy in large volumes, they will have greater decision-making capacity. This affects companies, since it is more difficult to obtain an adequate level of profitability, becoming a great threat to companies.
2. Bargaining power of suppliers
On the other hand, when suppliers have a lot of bargaining power, they have the ability to charge higher prices. The fewer suppliers there are in a market, the more bargaining power they have.
It can also be a threat to the company when there is little supply (from suppliers), few substitute products (from inputs) or when the company buys them in small quantities (from its suppliers). Suppliers increase their bargaining power, they could even monopolize the market. When faced with this problem, it is recommended that companies make their own raw materials, in order to have a guaranteed supply and a low cost.
3. Threat of entry of new competitors
The entry of new competitors to the market is determined by the level of investment required and by the existing barriers in the market. A market is more attractive when the level of investment required is lower than the cost of capital. Likewise, a market is more attractive the less barriers to entry exist.
Naturally, there are common barriers such as high taxes, difficult access to distribution channels, high (required) capital investments and lack of experience in the sector. The higher the barriers, the lower the level of threat from competition.
4. Appearance of substitute products
A substitute product is a strong competitor in the market for goods and services. Therefore, the more substitutes there are on the market at a lower price, the greater threat a company faces. Companies that have many competitors with substitute products must manage lower prices to attract consumers. You can also work to achieve product differentiation that gives them a competitive advantage.
5. Rivalry between competitors
Lastly, rivalry between competitors is the most important aspect when conducting a sectoral analysis. This, because it allows to elaborate a better definition of the sector to be able to find business opportunities. Rivalry between competitors becomes more intense when demand in a market decreases. There is also a lot of rivalry when there is not much differentiation between the products, when there are very high fixed costs and when there are a large number of competitors.
However, the degree of rivalry between competitors is decisive for obtaining profits within a sector. The more rivalry there is, the lower the degree of profitability. The less rivalry, the greater the possibility of obtaining better benefits. For that reason, companies must continuously innovate and improve their products, only then can a sustainable advantage be maintained.

To conclude, it can be stated that sector analysis is a very useful tool that guides companies in order to develop a sustainable competitive advantage over their competitors. The greater the information of the sector in which a company competes, the greater the possibility of designing better strategies that help take advantage of business opportunities. In the same way, threats can be better dealt with. All together, it improves productivity and the possibility of success for companies.
Leave a Reply