Competitor analysis

The analysis of the competition is the process that a company puts into practice to know how to act in the competitive environment, which begins by recognizing its competitors to determine what their main objectives, strategies, strengths and weaknesses are.
However, competitor analysis is a very important tool for any market-oriented company.
Undoubtedly, for companies to be successful in a highly competitive market, all decisions related to marketing strategies and tactics that they are going to implement must be based on the way their competitors act and react.
On the other hand, the most relevant aspects that companies should know about their competitors are based on knowledge about their products, prices, communication and distribution processes.
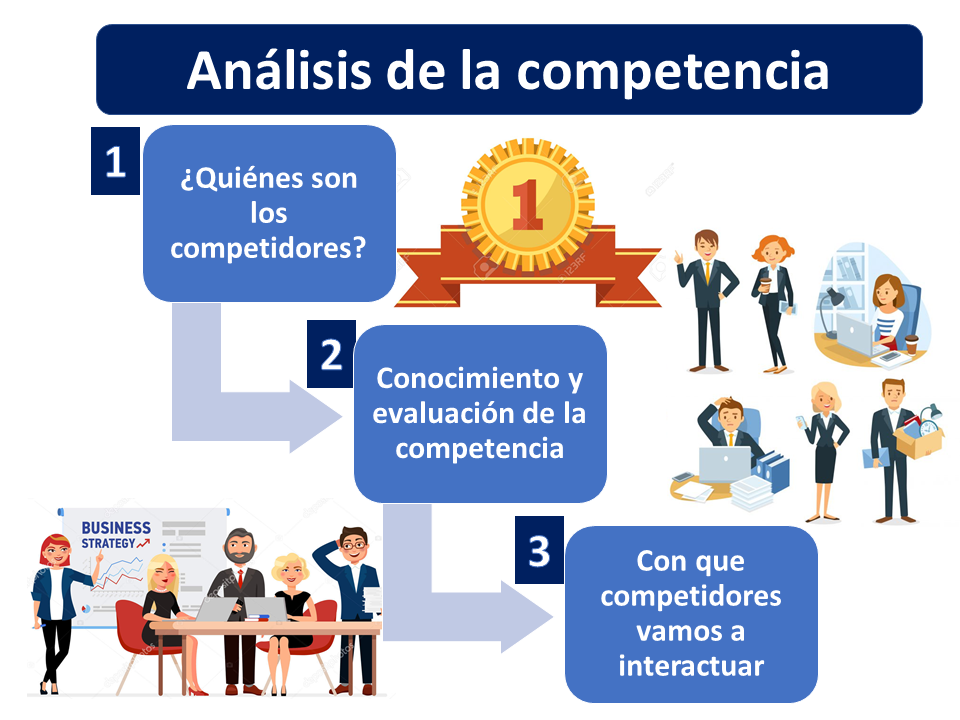
Steps in competitor analysis
Either way, the steps in the analysis of the competition are first to identify the competitors, then to know and evaluate their way of acting within the market and finely determine strategies of how we are going to defend ourselves or how we are going to face the competitors.
1. Who are the competitors?
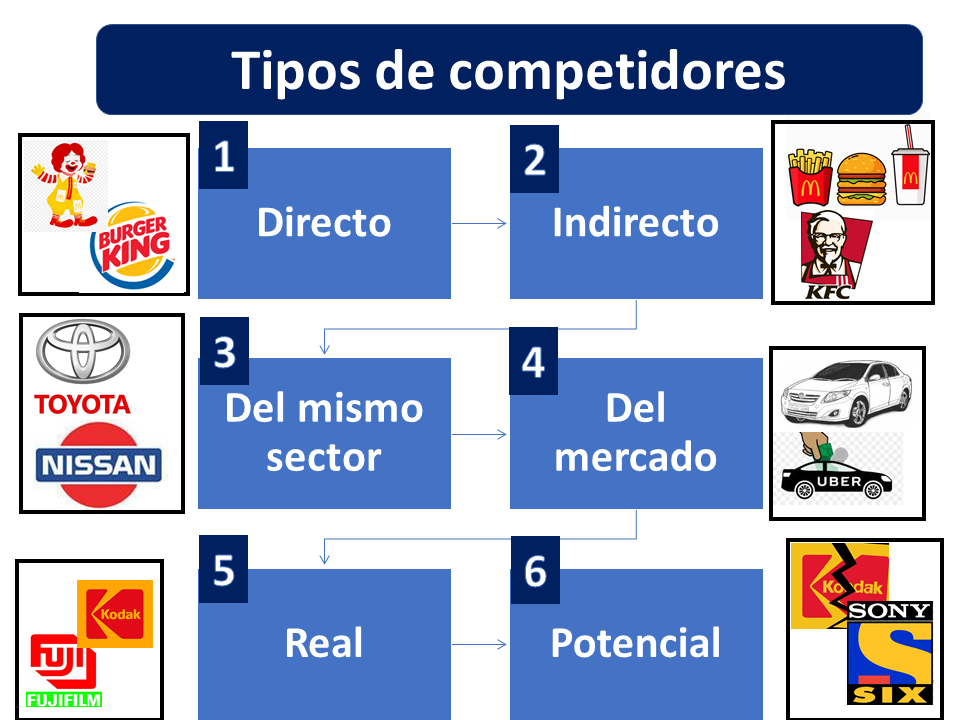
Every company can identify its competitors and classify them as follows:
to. Direct competitors
It turns out that direct competitors are all companies that produce a product very similar to ours, target the same market segment or use a pricing strategy very similar to ours.
For example, a direct competitor is the case of McDonald's and Burger King, since both companies produce hamburgers, the market segment is people who appreciate fast food services and their price level is very similar.
b. Indirect competitors
On the other hand, indirect competitors are all competitors that produce a product to meet the same need and as a consequence are seeking to obtain the consumer's preference and have income through the sales generated. They generally produce substitute products.
Indeed, in the case of McDonald's, we could consider Kentucky Fried Chicken as an indirect competitor, in this case both companies solve the need for consumer hunger, so it is a McDonald's competitor that hopes to keep it. consumer money facing that need.
c. Competitors from the same sector
Now a competitor considered within the same sector is one that produces goods and services within the same production sector.
In relation to the case of the automotive industry, the Toyota company competes with Nissan because they are competitors in the same sector. For this reason, any company that produces automobiles will be considered a competitor in the same sector.
d. Competitors within the market
Therefore, a competitor in the market is any company that produces any good or service to satisfy the same need.
That is, for the Toyota company, a market competitor turns out to be any company that produces a good or service that serves to cover the need for transportation.
Therefore, Toyota's competitor is the company Uber that offers travel services to the consumer through a technological application, the public transport service such as the subway and the taxi service, among some that can be named. In any case, all these companies solve the need for transportation for the user.
Of course, the competitor within the market greatly expands the competitive capacity of a company because it allows recognizing many more competitors and being more attentive to the actions and strategies they take and apply.
and. Real competitor
While a real competitor is any company that we can easily identify because they are currently competing in our market, it is easy to know them and know how they behave in the competitive environment.
F. Potential competitor
In the same way, the potential competitor is the most dangerous for a company, because as it is not yet present in the market, it is more difficult to know how it will act within the competitive environment and many times we are not prepared to face it.
Of course, there are many relevant cases in marketing such as Kodak that considered its biggest competitor to be Fuji and it turned out to be Sony with the introduction of digital cameras.
2. Knowledge and evaluation of the competence
The information that most interests a company about its competitors is the following:
to. The objectives and strategies
Above all, the objectives and strategies of each company make it possible to determine what they are giving greater importance to; that is, if what interests them is market share, profits, growth, technological or service leadership.
b. Strengths and weaknesses
Apparently, the knowledge of the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors allows us to better respond to their attacks when defending ourselves or if, on the contrary, we take the initiative to go against the competition, we know what are the weaknesses that we can take advantage of.
3. What competitors are we going to interact with?
This last step allows us to define what type of competitors we are going to interact with and thus adapt our marketing strategies to better respond.
Actually, when choosing which companies we are going to compete with, we can choose weak or subordinate competitors who are the ones who generally lose, since they have fewer resources and possibilities to compete.
On the other hand, if we choose strong or dominant competitors, these are the ones who usually win in the competitive context because they are better trained and have better possibilities to attack or defend themselves.
In any case, if a company truly wants to innovate and evolve, it is better that it chooses to compete with strong competitors, but it must also measure its strength not only to lose out.
Finally, for every company it is important to know its competition, because this allows them to better train themselves to react to an attack and to be able to defend themselves in the best possible way. If, on the contrary, the company takes the initiative to attack, it must be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of its competitor in order to make the best decisions on how to deal with it.
Leave a Reply