Aggregate demand
What is aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand consists of quantity of goods and services that consumers in a country require, for a certain price level and over a period of time.
This demand comes from the State, companies and families (economic agents) of a region. In addition, it is closely related to the GDP (gross domestic product) of the country, since they usually measure the same.
Because it depends on the goods and services that the beneficiaries usually want to buy, the aggregate demand can be accounted for specifically: is composed of the consumption (C), investment (I), public spending (G) and exports (X) net of a country.
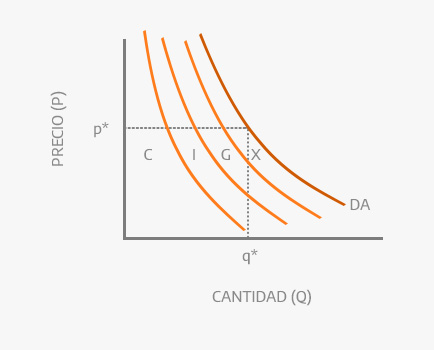
Aggregate demand graph.
Aggregate demand formula
To calculate aggregate demand, the following formula is usually used:

Aggregate demand formula.
The components that make up aggregate demand are as follows:
- C: consumption by families, even those made abroad.
- I: all investments made by companies in a country.
- G: public spending, that is, the amount of money a country spends.
- XM: net exports, i.e. exports (X) minus imports (M) from a country.
With this formula, we can conclude that aggregate demand is the gross domestic product of a country.
Determinants of aggregate demand
The factors that allow the aggregate demand to be carried out are the following:
- The consumer spending, which depends on the economic situation of the families, their income and interests.
- The public spending of a country.
- The investment by SMEs and private companies.
- The money supply of a country, that is, the amount of money it has available.
- The monetary and fiscal policy of a country.
Leave a Reply